Individuals pay income tax, whereas the companies in the UK come pay corporation tax. It is a regime that presents an entire system of taxation for companies.
The article will help you gain insight into the following:
- What is corporate tax?
- Who pays the corporate tax?
- Corporate tax rates
- Taxable profits?
- Taxation for resident and non-resident companies
- General and special corporation tax regime
- Diverted profit tax
- Registering for corporate tax
- How to file a tax return?
- Tax allowances & reliefs
- Corporate tax deadlines
- How to pay corporate tax?
- Corporate tax penalties
- Final thoughts
What is corporate tax?
Companies and individuals paid taxes alike until 1965, with an additional profits tax. Finance Act 1965 introduced corporation tax. Since then, the corporation tax system has undergone many systematic changes. It is projected that for the 2020-21 tax year, it accounts for circa £40 Billion, 5% of the UK’s total receipts.
The rate of corporation tax for all limited companies has been 19% since the year 2016. Companies don’t receive any tax-free allowance and must pay tax on all profits.
Need Corporate Accountant
Work with a London-based accountant for tax, accounting, payroll, & EIS/ SEIS needs.
Who pays the corporate tax?
You must pay corporate tax on profits from doing business as:
- A limited company
- A foreign company
- A club, co-operative, or other incorporated association
Corporate tax rates
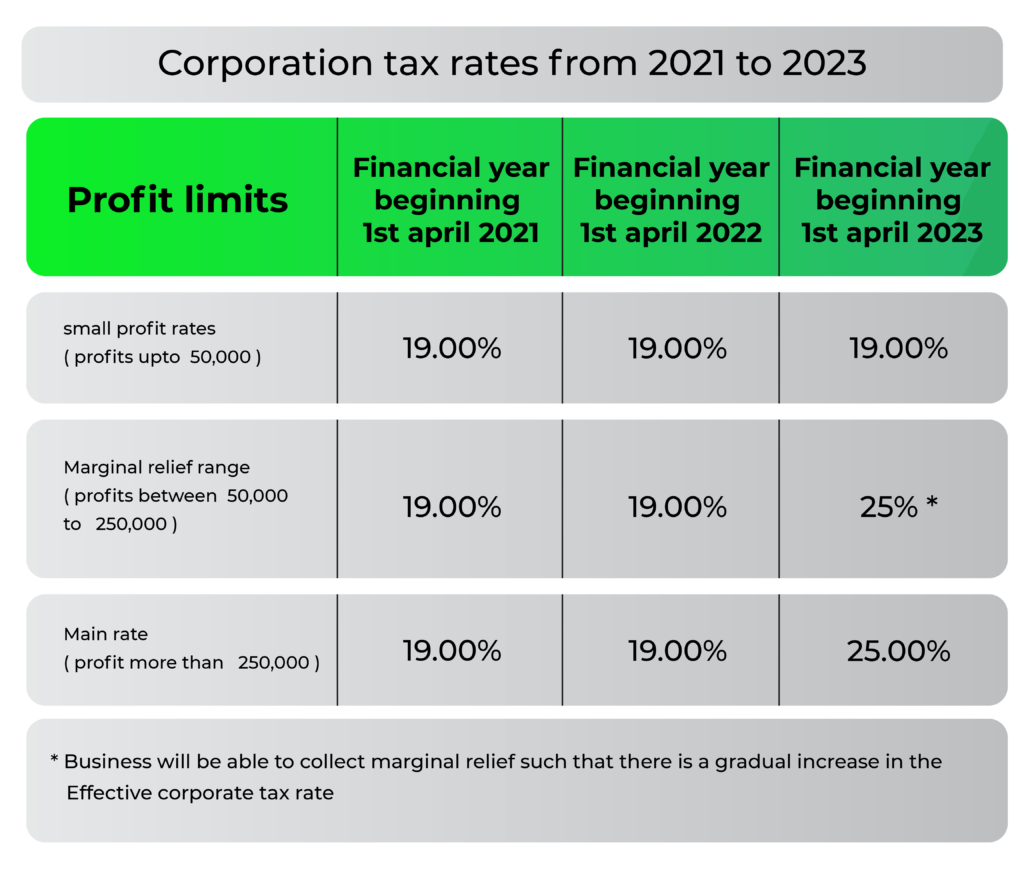
The corporation tax, which is currently at 19%, is expected to increase to 25% from 2023-24. Businesses having a profit of less than £50,000 will continue to be taxed at 19%. The table below presents a clear picture:
Taxable profits
Profits for corporation tax include the money company makes from:
- Doing business
- Investments
- Selling assets
Taxation for resident and non-resident companies
In the United Kingdom, you can describe tax structure in a very simplified manner. The division is made based on resident & non-resident companies.
Resident companies have to pay the tax on the profits they earn worldwide, while non-residents have to tackle UK-based profits.
General and special corporation tax regime
While examining the system, the essential aspects to consider are the taxes levied on corporate income, which are of two types general & special tax systems. After that, the prominent elements to look at are available & special rates along with other taxes.
| General Rates | 19% |
| Special Rates | No special provision apart from the below-mentioned companies: • Oil & gas company • Life insurance • Tonnage tax • Banking sector |
Oil & gas company
Profits that arise from oil or gas extraction, gas rights in the United Kingdom are subject to tax in the UK itself following rates of 2006, including a total rate of 30% and a low rate of 19%.
Life insurance company
Life Insurance also comes under different tax regimes, including different rates and rules for quantifying profits.
Tonnage tax
Companies that operate qualifying ships managed in the United Kingdom can choose to apply to the tonnage scheme. They need to tonnage tax in place of corporation tax. It replaces the tax-adjusted profit/loss on the shipping business.
Banking sector
An additional tax of 8% applies to companies in the banking sector over GBP 25 million. The loss utilization is also restricted; carried forward trading losses can be set against only 25% of profits.
Diverted profit tax (DPT)
DPT introduced in 2015 is a part of the UK’s response to the shifting tax environment and is separate from other taxes. It applies to diverted profits at the rate of 25%.
For accounting periods beginning on or after 1 April 2023, it will rise to 31%.
It may apply in two cases:
- Where companies create a tax benefit by making transactions lacking economic substance.
- Where foreign companies are operating to avoid setting up a UK permanent establishment.
The list of situations not within the scope of DPT are:
- The parties are small or medium-sized businesses
- Tax mismatch arises from loan relationships
- Receipt of payments by pension funds, charities, investment funds, and the person with sovereign immunity.
Registering for corporation tax
A company is automatically registered with the HMRC for corporate tax. Alternatively, you must tell HMRC within three months of incorporation.
At the time of registration; you will need to include the following details:
- The date of starting a business
- Company name and registration number
- Company’s registered office address
- Type of business
- The date up to which you will make your annual accounts
- Name and address of company directors
Upon successful registration, you will get a Unique tax reference number, also known as UTR.
If you are registering late, you get a penalty. So make sure that you register your business within the deadline.
How to file a tax return?
A company must calculate its tax, like other forms of business.
You will need to complete a company tax return known as form CT600. The form must contain:
- Company name
- Company registration number
- Company UTR
- Registered office
- Income and expense details
- Tax calculation
- Allowances and reliefs
- The name, capacity of the person approving the return
- Bank details- if you return is that of a refund claim
Check our guide on Common Tax mistakes that business owners make.
Tax allowances and reliefs
There are allowances while working out your taxable income. The costs of running a business can be deducted from the revenue.
Examples of allowable expenses include employee salaries, travel, rent, and accountant’s fees. Expenses incurred wholly & exclusively for business purposes are allowable.
Following corporate tax reliefs available to minimise your tax bill:
- Research & Development Relief- If the company works on innovative projects in science and technology
- Patent Relief- A lower rate applies to profits earned from inventions & innovations.
- Creative Industry Tax Relief- Companies in the creative industries claim a larger deduction while calculating profits.
- Terminal, Capital, and Property Income Losses- You are eligible if you lose from the trading, sale, or disposal of a capital asset or property income.
- Marginal Relief- It is available only if the profits are between £300,000 and £1.5 million before 1 April 2015.
- Relief Of Goodwill and relevant assets- You can also get relief on the purchase of goodwill & relevant assets.
Need Corporate Accountant
Work with a London-based accountant for tax, accounting, payroll, & EIS/ SEIS needs.
Corporate tax deadlines
This is where corporate tax gets complicated as the payment deadline is different from other taxes and depends on the accounting period. The crucial points to keep in mind are:
- You need first to pay corporation tax before tax return.
- The deadline to pay tax is nine months and one day after the end of your accounting period.
- The deadline to submit the tax return is twelve months after the end of the accounting period.
- You may have two accounting periods because your accounting period is longer than 12 months.
For example,If you set up a company on 10 January 2021, the first accounting period will be up from 10 January 2021 to 31 January 2022.
Your first tax period will usually be from 10 January 2021 to 09 January 2022, and the second tax period will be from 10 January 2022 to 31 January 2022.
Just remember, the tax return CT600 period cannot exceed 365 days except where there is a leap year.
- Businesses with more than £1.5 million in profits will need to pay their Corporation Tax in installments.
| Corporation Tax Due | Corporate Tax Return Due |
| Nine months and one day later | 12 months later |
How to pay corporate tax?
There are various ways to pay your corporation tax bill. The timelines for paying tax are as follows:
| For payments on same day/next day | • CHAPS • Online Banking • Telephone Banking |
| Allow three working days | • BACS • Online Payment by Direct Debit |
| Allow five working days | • Direct Debit |
For details, check out our blog post on Paying Companies House and HMRC penalties.
Corporate tax penalties
If you are submitting a late tax return, HMRC has the power to fine you. The following penalties are for those who file a late company tax return:
| The penalties in case of default are as follows: | |
| Time after deadline | Penalty |
| 1 day | £100 |
| 3 months | Another £100 |
| 6 months | 10% of the estimated unpaid tax |
| 12 months | Another 10% of any unpaid tax |
Final thoughts
UK Corporate taxonomy is long and can be tricky at times. To minimise your tax bill, careful planning is essential. Make sure you have a tax expert on board from day one.